TimeStretch
- class audioflux.TimeStretch(radix2_exp=12, slide_length=1024, window_type=WindowType.HANN)
Time stretch algorithm
- Parameters
- radix2_exp: int
fft_length=2**radix2_exp- slide_length: int
Window sliding length.
- window_type: WindowType
Window type for each frame.
See:
type.WindowType
Examples
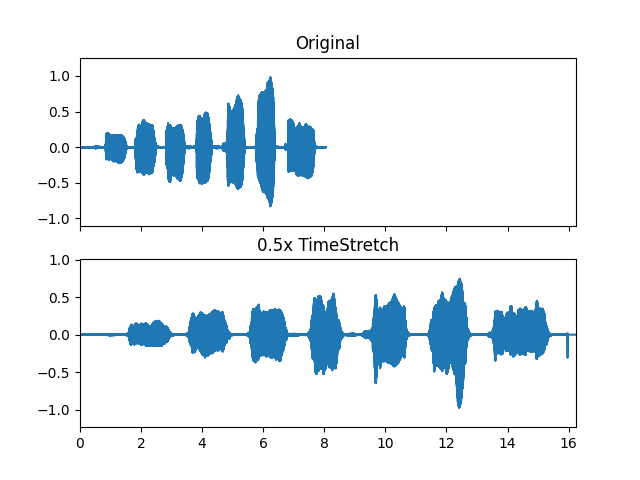
Read voice audio data
>>> import audioflux as af >>> audio_path = af.utils.sample_path('voice') >>> audio_arr, sr = af.read(audio_path)
Compute the time stretch
>>> time_stretch_obj = af.TimeStretch(radix2_exp=12, window_type=af.type.WindowType.HANN, slide_length=1024) >>> new_audio_arr = time_stretch_obj.time_stretch(audio_arr, 0.5) >>> # af.write('./audio_arr_0_5.wav', new_audio_arr, sr)
Show plot
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, sharex=True) >>> ax = af.display.fill_wave(audio_arr, sr, axes=axes[0]) >>> ax.set_title('Original') >>> ax = af.display.fill_wave(new_audio_arr, sr, axes=axes[1]) >>> ax.set_title('0.5x TimeStretch')
Methods
cal_data_capacity(rate, data_length)Calculate the data capacity.
time_stretch(data_arr, rate)Compute the time stretch
- cal_data_capacity(rate, data_length)
Calculate the data capacity.
- Parameters
- rate: float
Time stretch rate
- data_length: int
Input array length
- Returns
- out: int
- time_stretch(data_arr, rate)
Compute the time stretch
- Parameters
- data_arr: np.ndarray [shape=(…, n)]
Audio data array
- rate: float
Time stretch rate
- Returns
- arr: np.ndarray [shape=(…, n1)]