Harmonics
- class audioflux.Harmonic(radix2_exp=12, samplate=32000, slide_length=1024, window_type=WindowType.HAMM, low_fre=27.0, high_fre=4000.0)
Harmonics
- Parameters
- radix2_exp: int
fft_length=2**radix2_exp- samplate: int
Sampling rate of the incoming audio.
- slide_length: int
Window sliding length.
- window_type: WindowType
Window type for each frame.
See:
type.WindowType- low_fre: float
Lowest frequency. Default is 27.0.
- high_fre: float
Highest frequency. Default is 4000.0.
Examples
Read guitar_chord2 audio data
>>> import audioflux as af >>> audio_path = af.utils.sample_path('guitar_chord2') >>> audio_arr, sr = af.read(audio_path)
Compute harmonic_count
>>> hr_obj = af.Harmonic(radix2_exp=12, samplate=sr, slide_length=1024, window_type=af.type.WindowType.HAMM) >>> count_arr = hr_obj.harmonic_count(audio_arr, 82, 900)
Show harmonic_count plot
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, figsize=(16, 9), sharex=True) >>> af.display.fill_wave(audio_arr, axes=axes[0]) >>> times = np.arange(count_arr.shape[-1]) * (hr_obj.slide_length / sr) >>> af.display.fill_plot(times, count_arr, axes=axes[1], label='Harmonic Count')
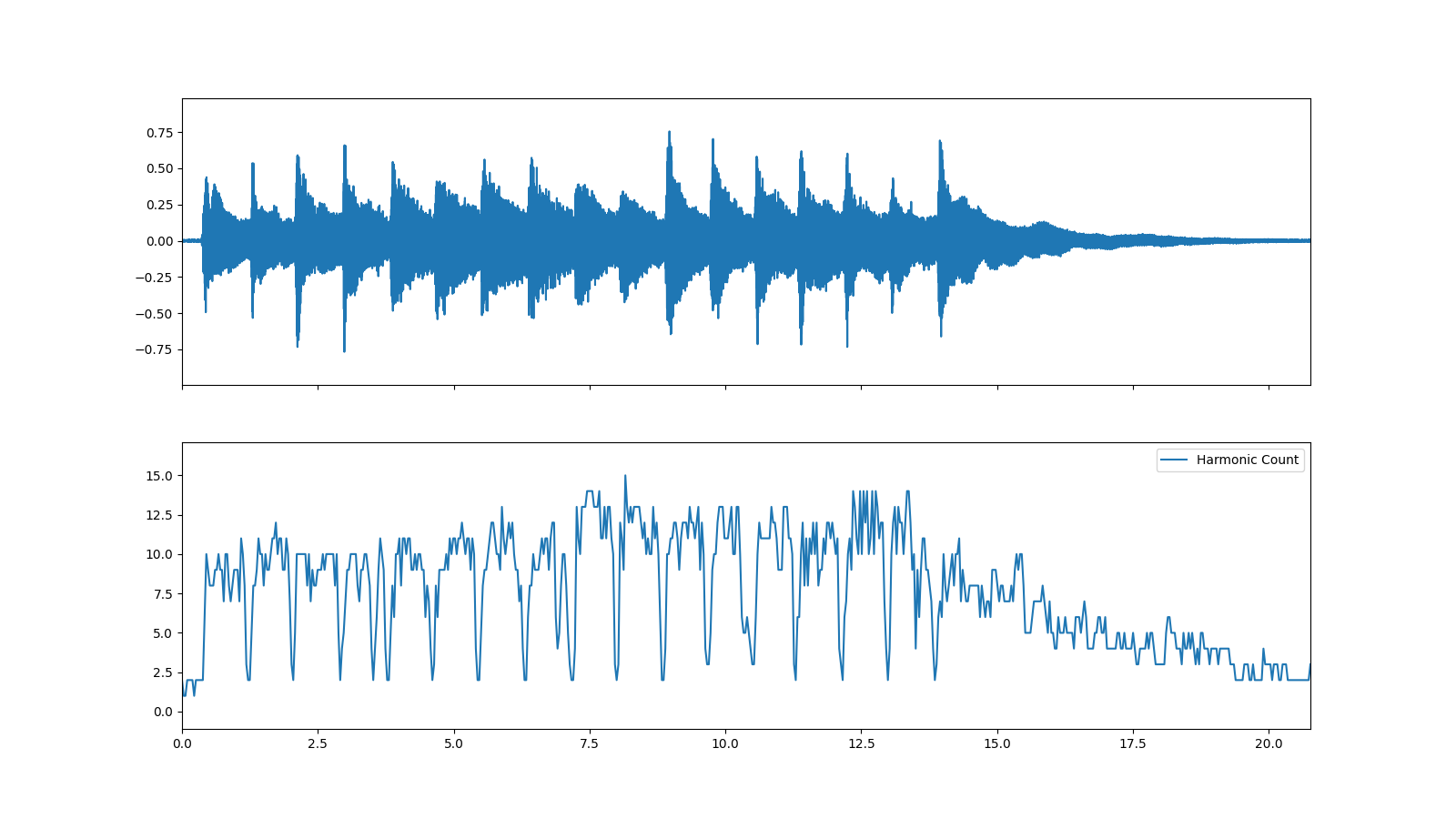
Methods
cal_time_length(data_length)Calculate the length of a frame from audio data.
harmonic_count(data_arr, low_fre, high_fre)- Parameters
- cal_time_length(data_length)
Calculate the length of a frame from audio data.
fft_length = 2 ** radix2_exp(data_length - fft_length) // slide_length + 1
- Parameters
- data_length: int
The length of the data to be calculated.
- Returns
- out: int
- harmonic_count(data_arr, low_fre, high_fre)
- Parameters
- data_arr: np.ndarray [shape=(…, n)]
Input data array.
- low_fre: float
Lowest frequency.
- high_fre: float
Highest frequency.
- Returns
- out: np.ndarray [shape=(…, time)]
Harmonic count array.
- class audioflux.HarmonicRatio(samplate=32000, low_fre=32.70319566257483, radix2_exp=12, window_type=WindowType.HAMM, slide_length=1024)
Harmonic Ratio
- Parameters
- samplate: int
Sampling rate of the incoming audio.
- low_fre: float
Lowest frequency.
- radix2_exp: int
fft_length=2**radix2_exp- window_type: WindowType
Window type for each frame.
See:
type.WindowType- slide_length: int
Window sliding length.
Examples
Read guitar_chord2 audio data
>>> import audioflux as af >>> audio_path = af.utils.sample_path('guitar_chord2') >>> audio_arr, sr = af.read(audio_path)
Compute harmonic_count
>>> hr_obj = af.HarmonicRatio(radix2_exp=12, samplate=sr, slide_length=1024) >>> ratio_arr = hr_obj.harmonic_ratio(audio_arr)
Show harmonic_count plot
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, figsize=(16, 9), sharex=True) >>> af.display.fill_wave(audio_arr, axes=axes[0]) >>> times = np.arange(ratio_arr.shape[-1]) * (hr_obj.slide_length / sr) >>> af.display.fill_plot(times, ratio_arr, axes=axes[1], label='Harmonic Ratio')
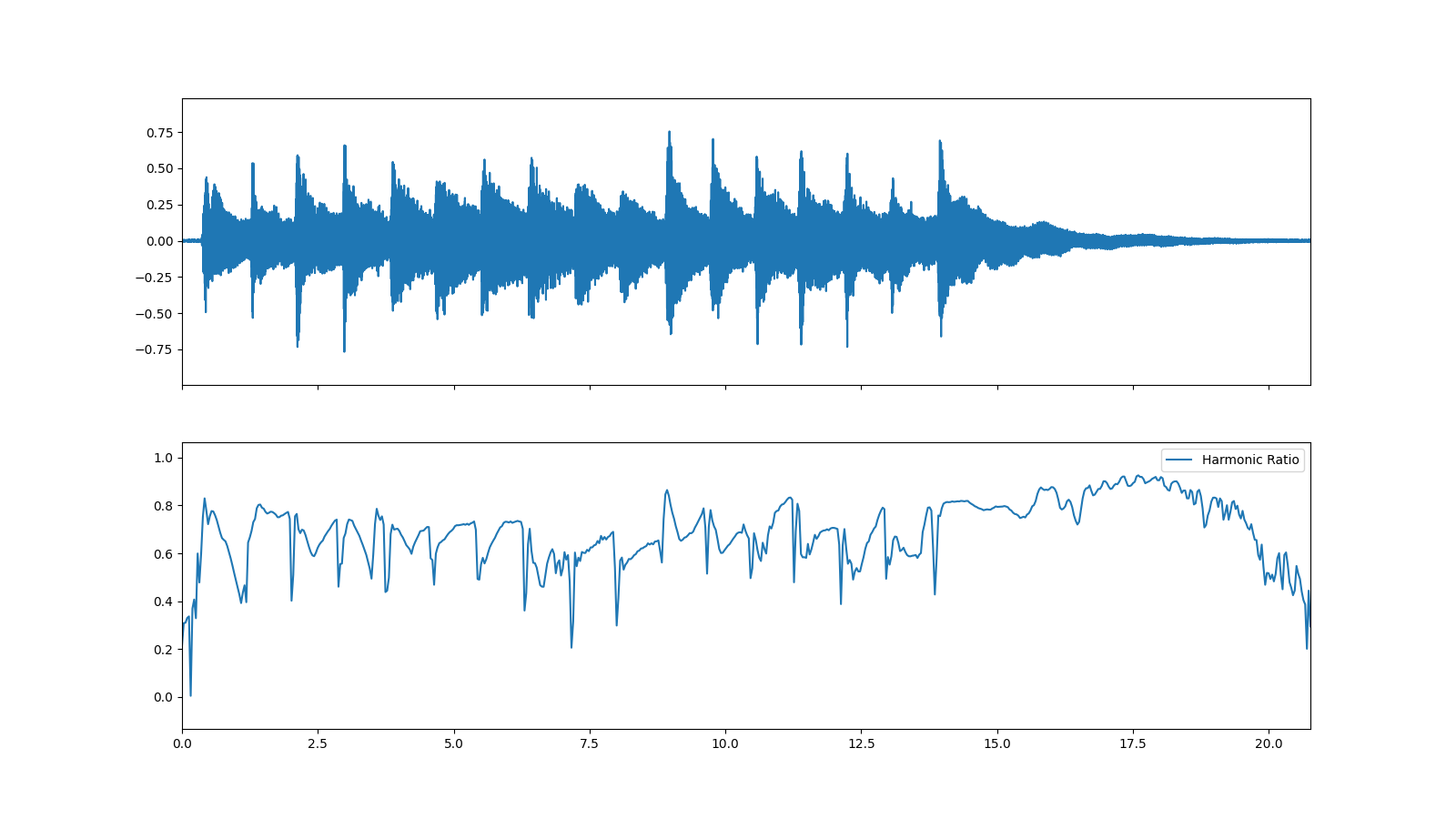
Methods
cal_time_length(data_length)Compute the time length
harmonic_ratio(data_arr)Compute harmonic ratio
- cal_time_length(data_length)
Compute the time length
- Parameters
- data_length: int
Input array length
- Returns
- out: int
- harmonic_ratio(data_arr)
Compute harmonic ratio
- Parameters
- data_arr: np.ndarray [shape=(…, n)]
Input audio data array.
- Returns
- out: np.ndarray [shape=(…, time)]